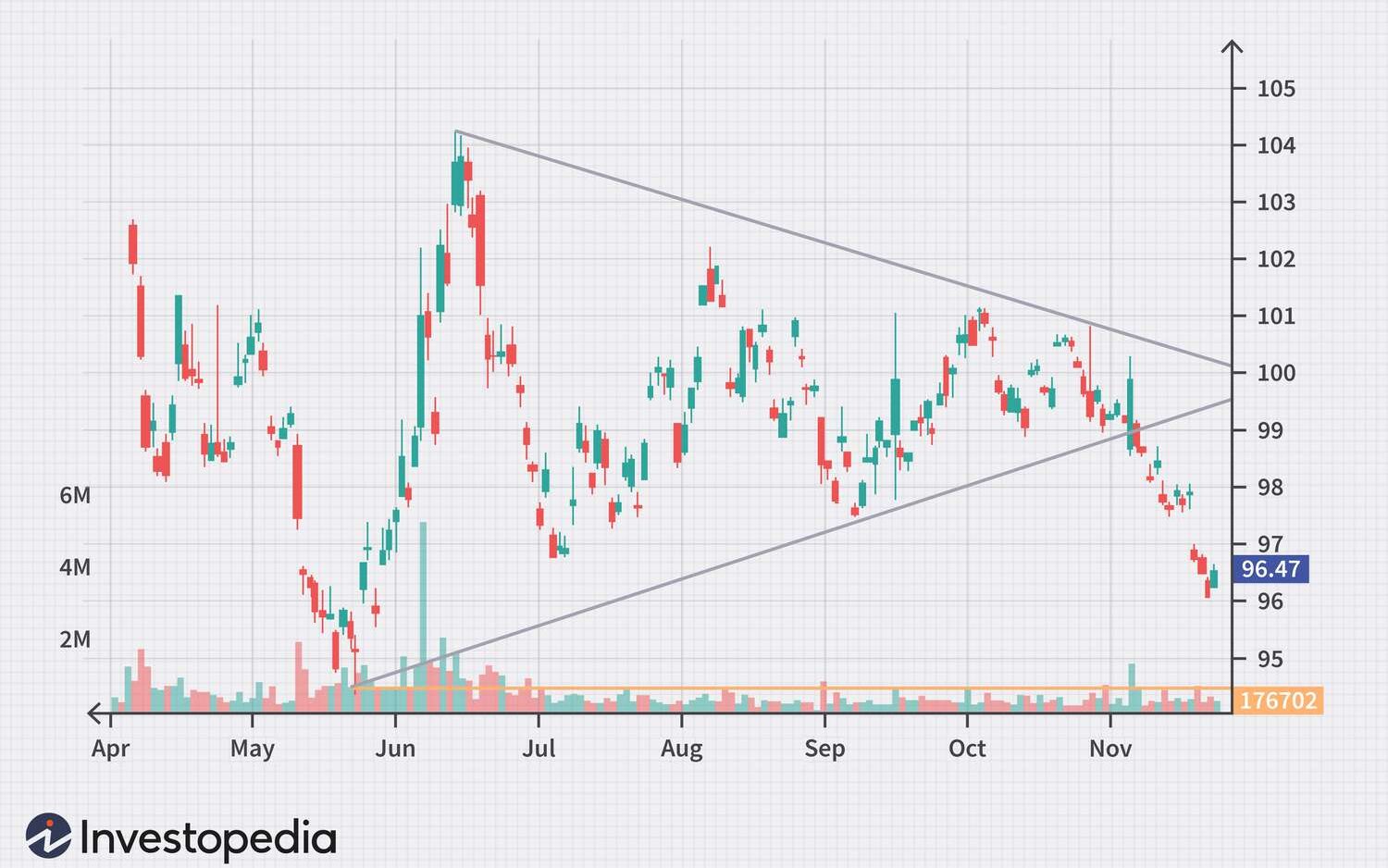
Stock Exchange Chart Patterns.
Image Credit: Investopedia.com
How to Invest in Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide
Investing in stocks is a powerful strategy for building wealth over time, but success requires a solid understanding of the stock market and the factors influencing individual stocks. In this article, we’ll delve into the basics of stock investing, covering how to get started, the types of stocks available, and essential strategies for maximizing returns.
Topics:
- Introduction (What are stocks?)
- Types of Stocks
- What is Stock Market and How does it work?
- Getting Started in Stock investing
- Investment strategies for Stock investing
- The Risk Associated with Stocks Investing
- Managing Risk When Investing in Stocks
- Conclusion

Credit: Canva.com
What Are Stocks?
Stocks, also known as equities or shares, symbolize ownership in a company. As a shareholder, purchasing a stock grants you voting rights on certain company decisions and a potential share of profits through dividends.
When a company seeks to raise capital, it can issue stocks to investors through an Initial Public Offering (IPO) or secondary offerings.
Types of Stocks
There are two main types of stocks: common stock and preferred stock. Common stock provides ownership, voting rights, and dividends. Preferred stock, while lacking voting rights, typically has a higher claim on a company’s assets and earnings.
Further categorizations include:
- Growth Stocks: These companies are expected to experience rapid future growth, often due to the introduction of new products or services. While growth stocks offer higher return potential, they are also riskier due to increased sensitivity to market fluctuations.
- Value Stocks: Undervalued companies with the potential to increase in value over time characterize value stocks. Typically, these are mature companies with steady profits and a track record of stability.
- Dividend Stocks: These stocks pay regular dividends to shareholders, providing a steady income stream. Investors often seek dividend stocks for a combination of income and potential stock appreciation.
What is the Stock Market and How Does it Work?
A stock market is where investors buy and sell stocks, representing ownership in publicly traded companies. Exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ serve as marketplaces for trading stocks.
Stock prices depend on supply and demand. If more people want to buy than sell, prices rise, and vice versa. Various factors, such as a company’s financial performance and overall economic conditions, influence stock prices.
Getting Started in Stock Investing
For novices, opening a brokerage account is the first step. Choose from online platforms like Robinhood and E TRADE, or traditional firms like Charles Schwab and Fidelity. Consider account type, fees, and available investment products. After funding your account, you can start buying and selling stocks.
Before diving in, establish a clear investment plan, considering financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Diversify your portfolio by investing in different stocks and asset classes like bonds and cash.
Investment Strategies for Stock Investing
Various strategies cater to different financial goals and risk tolerance:
- Value Investing: This strategy involves buying undervalued stocks based on their intrinsic value. Value investors anticipate that the stock price will eventually catch up to the company’s true worth.
- Growth Investing: Growth investors focus on companies experiencing or expected to experience rapid growth. These companies may not be profitable yet, but they have strong potential for future growth.
- Income Investing: Income investors seek regular income through dividends. They may invest in stocks with a history of steady dividend payments or in companies with the potential to increase their dividends over time.
- Index Investing: This strategy involves buying a basket of stocks that represents a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. The idea is that the performance of the overall market is a better indicator of long-term returns than the performance of any individual stock.
- Active Investing: Active investing requires actively buying and selling stocks in an attempt to outperform the market. This strategy demands time and effort and may not be suitable for all investors.
The Risk Associated with Stocks Investing
Investing in stocks involves inherent risks, categorized as:
- Market Risk: This refers to the risk that the value of an investment will decline due to changes in the market or economic conditions. This type of risk is inherent in all investments and is impossible to completely eliminate.
- Company-Specific Risk: This refers to the risk that a particular company will experience financial difficulties or negative events that could affect its stock price. Diversification helps manage this type of risk.
- Liquidity Risk: This refers to the risk that an investor will not be able to sell an investment when needed or will have to sell at a loss due to a lack of buyers. This risk is more prevalent in stocks that are not widely traded.
- Inflation Risk: This refers to the risk that the value of an investment will decline due to inflation. Investments that do not offer protection against inflation, such as cash and fixed-income investments, are more susceptible to this risk.
- Interest Rate Risk: This refers to the risk that the value of an investment will decline due to changes in interest rates. This risk is more prevalent in fixed-income investments, such as bonds.
Europe and US Markets are gone up quite fast and too much
— Markets Today (@marketsday) February 29, 2024
Unprecedented flow of easy money keeps Market stocks on bull run….
Market valuations are too high. They need are looking for an excuse to fall.
The stock market is not the economy.
"Greed is not always good" pic.twitter.com/rYy8cLjeqx
Managing Risk When Investing in Stocks
Strategies to manage risk include:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across a variety of different stocks and sectors helps reduce risk. By diversifying your portfolio, you can help minimize the impact of any one investment on your overall portfolio.
- Asset Allocation: This refers to the process of dividing your portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. By allocating your investments among different asset classes, you can help reduce risk and improve your chances of success.
- Risk Tolerance: Understanding your own risk tolerance is important when it comes to managing risk when investing in stocks. Different investors have different levels of risk tolerance, and it’s crucial to invest in a way that aligns with your personal risk tolerance.
- Risk Management Tools: Various risk management tools, including stop-loss orders, margin, and options, can be employed to help manage risk. It’s important to understand how these tools work and to use them appropriately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, investing in stocks presents opportunities for wealth growth, but understanding and managing risks are crucial. Diversifying your portfolio, considering asset allocation, and knowing your risk tolerance are essential elements of successful stock investing. Employing risk management tools further enhances your ability to navigate the dynamic stock market. A well-thought-out plan and staying informed about market conditions are keys to successful stock investing. Remember, the journey of investing is as much about managing risks as it is about maximizing returns.
References:
Feedback: